eXtremeDB HA Applications
Two-layered architecture
eXtremeDB High Availability uses a two-layered architecture that facilitates the development of HA-enabled eXtremeDB-based applications. The higher layer is called the protocol layer. This layer is responsible for the high availability logic of the application. The lower layer is called the transport or network layer which implements the actual transmission of data between the master and replica nodes.
Applications use the higher layer protocol API to implement high availability. The protocol layer uses the transport layer API to send and receive data between network nodes so that application developers normally do not need to interact with the lower level API. Only if implementing a custom transport layer will the developer be concerned with these lower layer functions.
Application structure
Several host language APIs are provided to incorporate eXtremeDB High Availability functionality. The C/C++, Java and C# APIs are described below. It is also possible to use xSQL to act as an HA master or replica application. (For more information and instructions on using the xSQL please refer to the xSQL User's Guide.)
To incorporate eXtremeDB High Availability:
C / C++
To incorporate eXtremeDB High Availability, C/C++ applications need to do the following:
1. Include
mcoha.hinto the application sources2. Declare an
auto_oidin the database schema3. Link with two libraries that implement the
protocol layer(HA) and thetransport layer(NW)4. Link with the serialization library
libmcoseri.aorlibmcoseri_debug.a.
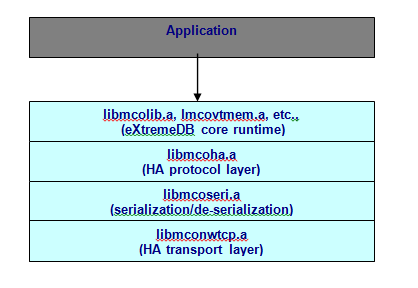
The protocol layer is implemented in the
mcohalibrary (libmcoha.afor Unix,mcoha.libfor Windows), and the platform-independent transport layer is implemented in a library with the namemconwXXX(libmconwXXX.afor Unix,mconwXXX.libfor Windows) where the “XXX” indicates the type of network protocol used. And more than one transport layer library may be linked with a single eXtremeDB High Availability application.The following network transport layer protocols are provided with eXtremeDB High Availability:
TCP:libmconwtcp.afor Unix,mconwtcp.libfor Windows
UDP:libmconwudp.afor Unix,mconwudp.libfor WindowsNamed Pipes:
libmconwpipes.afor Unix,mconwpipes.libfor WindowsQNX Messaging:
libmconwqnxm.a(only for QNX OS).To initialize eXtremeDB High Availability, all C and C++ applications must call
mco_HA_start()to start the HA runtime andmco_HA_channel_implementation_add()to register one or more NW channels. For example... mco_runtime_start(); mco_HA_start(); mco_HA_channel_implementation_add(mco_nw_tcpip_vt()); ...C#
To incorporate eXtremeDB High Availability, C# applications need to:
1. Include the eXtremeDB namespace (
using ExtremeDB;) in application sources2. Set the
HighAvailabilitySupportflag in the constructor of Database object to cause the HA support library to be dynamically loadedJava
To incorporate eXtremeDB High Availability, Java applications need to:
1. Include the eXtremeDB namespace (
import com.mcobject.extremedb.*;) in application sources2. Set the
HighAvailabilitySupportflag in the constructor of Database object to cause the HA support library to be dynamically loaded
Replication Data flow
The following diagram illustrates the basic eXtremeDB High Availability application data flow:
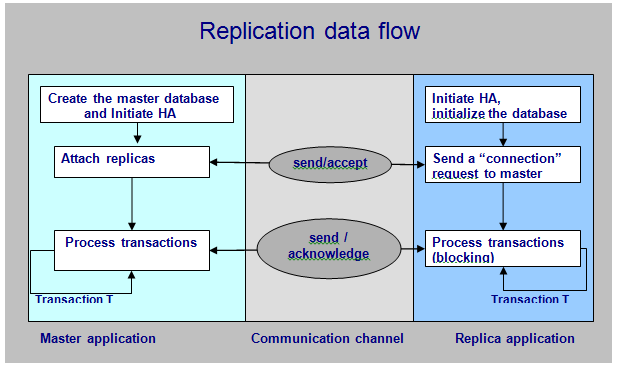
eXtremeDB High Availability applications may use
synchronousorasynchronousreplication and will normally implementhot switchlogic where the master and replica will be copies of the same application, aware that they are operating as master or replica, with the replica able to switch roles if necessary. All of the replication functionality is managed internally by the eXtremeDB High Availability runtime, though additional custom processing can be implemented in replicas by responding to specific replication events.The eXtremeDB High Availability runtime does the initial synchronization in the master application during the C/C++ function
mco_HA_attach_replica(), in C# or Java applications theMasterConnection.AttachReplica()method, and in replicas during the C/C++ functionmco_HA_attach_master(), in C# or Java applications theReplicaConnection.AttachMaster()method. After the initial synchronization, replication is managed synchronously or asynchronously by the eXtremeDB High Availability runtime when the master calls the C functionmco_trans_commit(), in C# or Java applications theMasterConnection.CommitTransaction()method.The management of the communications channel operations inside, asynchronous buffer processing and other important internal functions within the eXtremeDB High Availability runtime are controlled by timeout values set in C application in the
mco_HA_master_param_tstructure values passed to functionmco_HA_set_master_params()and themco_HA_replica_param_tstructure values passed to functionmco_HA_attach_master(). In C# and Java applications these timeouts values are properties of the MasterConnection.Parameters and ReplicaConnection.Parameters classes and are set in the master by calling theMasterConnection.SetReplicationMode()method; in replicas by theReplicaConnection.AtachMaster()method.DDL requirements
The schema for a C/C++ application using a database that might be replicated in HA mode must include the
auto_oiddeclaration.declare auto_oid [100000];In C# and Java applications the
auto_oidimplementation is automatic when a database instance is created by invoking the Database class constructor with High Availability support. In C# this is done as follows:Database db = new Database( …, Database.Mode.HighAvailabilitySupport);In Java the
MCO_CFG_HA_SUPPORTflag is specified as follows:Database db = new Database( Database.MCO_CFG_HA_SUPPORT );
Whether the database actually participates in the HA synchronization is determined at run-time. When the data definition is compiled for HA, the eXtremeDB High Availability DDL compiler inserts an 8-byte unique identifier (called
auto_OID, not to be confused with the field typeautoid) into each object. Thisauto_OIDis used by the runtime in the standby application to perform a synchronized commit outside the master application’s address space. Think of it as a global object identifier. A hash index is maintained for it, so the replica runtime can locate objects quickly when necessary.(These implementation details are provided for information value only. There is no published interface to access the index).
Initial Synchronization
The first step in replication is initial synchronization which is managed by the eXtremeDB High Availability runtime. On the master side this happens in C/C++ applications when the function
mco_HA_attach_replica()is called; in C# and Java applications theMasterConnection.AttachReplica()method. In the replica initial synchronization happens during its call to the C/C++ functionmco_HA_attach_master()or the C# or JavaReplicaConnection.AttachMaster()method.There are four ways to initially synchronize all newly attached replicas:
static,hot, withBSEandstateful. The differences between these modes are described in the Synchronization page. In C/C++ applications, the master application chooses the mode by settingmode_flagselement in themco_HA_master_params_tstructure. In C# and Java applications the mode is set in theMasterConnection.Parameterspassed to theMasterConnection.SetReplicationMode()method.Note that though it is not possible to combine the
staticandhotmodes, other modes can be combined.