Introduction to eXtremeDB Cluster
eXtremeDB Cluster is a distributed database implementation. Instances of applications can run on different nodes in a network, and all database modifications will be automatically replicated between all instances. For example, the following diagram illustrates a 5-node cluster.
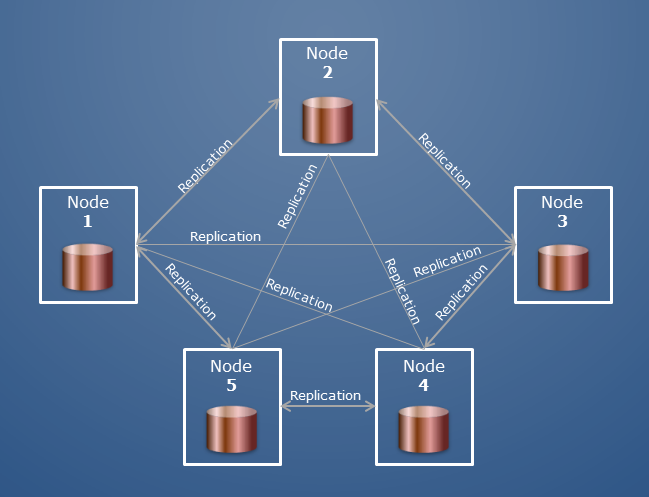
All nodes in a cluster hold the same copy of the database. All nodes in a cluster are equal, i.e. eXtremeDB Cluster has no dedicated master or replica nodes (as with eXtremeDB High Availability). Each node can perform
READ_WRITEandREAD_ONLYoperations.READ_ONLYtransactions are local, i.e. they don't require network operations, and run as fast as with a standalone database.Theory of operation
To update a database, a two-phase commit protocol is used. All operations are local, no network communications are involved, until the transaction is committed. The update scenario is as follows:
1. The thread running on the cluster node (called the initiator) performs a call to the C/C++ function
mco_trans_commit(), or the Java/C#ClusterConnection.CommitTransaction()method, for aREAD_WRITEtransaction.2. Internally the eXtremeDB Cluster implementation of the transaction commit invokes
commit_phase1()for the initiator database copy. Ifcommit_phase1()fails, the transaction is aborted and rolled back locally. (No network communication happens.)3. If the
commit_phase1()succeeds, the transaction is serialized and sent to all other nodes (called participants) in the Cluster.4. Each participant opens a transaction, applies the serialized data from the initiator and performs
commit_phase1().5. The results of these operations (
SUCCESSorFAIL) are sent back to the initiator.6. The initiator gathers replies from all participants and decides how to complete the global transaction:
- If all participants report
SUCCESS, the initiator completes the local transaction withcommit_phase2()and sendsCONFIRMmessages to participants.- If at least one participants replied with
FAIL, the initiator rolls back the transaction and sendsREJECTmessages to the participants.- Depending on the type of message (
CONFIRMorREJECT), participants performcommit_phase2()orrollback()to complete the transaction.Accordingly, database changes are either applied to all nodes, or rolled back. Since pessimistic locking is extremely expensive and subject to unpredictable failure-points when implemented in a network environment, eXtremeDB Cluster employs only the MVCC transaction manager.
The eXtremeDB Cluster implementation automatically controls the availability of nodes using timeouts and keep-alive messages. If a number of nodes become unavailable (i.e. there is no quorum), the processing of
READ_WRITEtransactions may be suspended.The schema for a C/C++ application using a database that participate in the cluster must include the auto_oid declaration.
Terminology
The term Node Address refers to a character string containing the transport-layer-dependent address of a node. For example, a node address for the
TCP/IPtransport could be<hostname>:<port>or<IP-address>:<port>. (See examples below.)The term Node Quorum Rank refers to an integer value that is used to determine whether enough interconnected nodes are online to work. If the sum of the
qrankvalues for nodeAand all nodes connected toAis more than half of the sum of theqrankvalues for all cluster nodes (online and offline), then nodeA(and other nodes online) will continue to work.It is helpful to consider two node quorum rank example scenarios:
1. All nodes have the same
qrankvalue: in this case the cluster will work if more than half of the nodes are active and connected to each other. If the cluster is split exactly in half, the cluster will not work.2. One node (call it
main) has aqrankvalue of 1, all other nodes have aqrankvalue of 0: in this case the cluster of nodes connected tomainwill always work. If themainnode dies, the cluster ceases to work.Note that in any scenario, if the cluster nodes split into several disconnected parts,
WRITEoperations will be allowed only for one of these parts
Overview
eXtremeDB Cluster is built on the eXtremeDB High Availability technology. However, while eXtremeDB High Availability provides the synchronization / replication support in a master-replica scenario, eXtremeDB Cluster provides a simple interface for managing a peer-to-peer network of “equal” nodes.
As a new node is connected to the cluster, it is synchronized in
hotmode, i.e. the newly connected node receives synchronization data and transactions from other nodes. Other currently connected cluster nodes can still performREAD_WRITEtransactions during the startup synchronization of the new node. (The new node selects the active node with the largest number of completed transactions at the moment of connection to perform the synchronization. If all the cluster nodes are equallyloadedwith completed transactions, then the synchronizer node is selected randomly from the active cluster nodes.)