eXtremeDB ODBC DSN configuration on Windows systems
Please use these links to view an overview of the eXtremeSQL ODBC implementation and installation steps. Below are presented the steps to configure the McObject ODBC driver to connect to eXtremeSQL applications.
The McObject ODBC Setup dialog can be used to configure a DSN for local or remote connections.
The Setup Dialog looks like the image below:
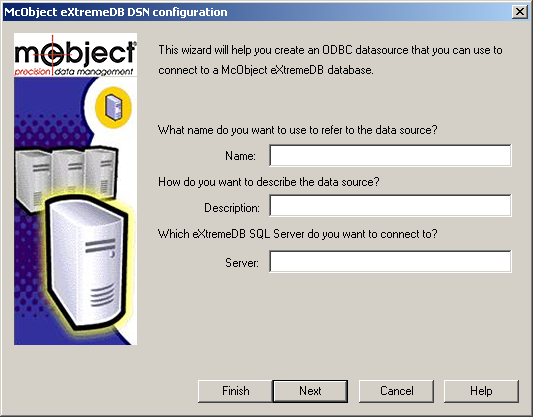
Connecting to a local database
To connect to a database on the current computer, enter the name of the database as it is passed to the
engine.open()ormco_db_open_dev()function calls in the server application, an optional description and specify that the server is on this computer (localhost) and the port (eg. 5001) that it is listening on. The example below specifies thetpcdbdatabase used by the SDK samplessamples\native\sql\tpcandodbc\samples\tpcodbc:
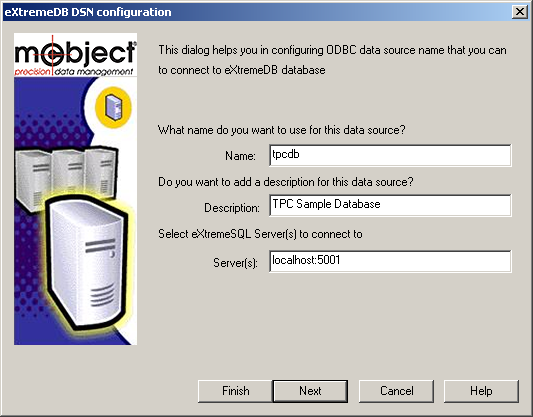
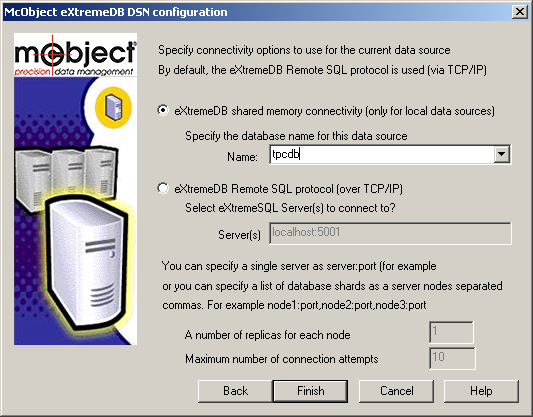
Pressing next brings up the following screen to specify whether this is a local or remote connection. Naturally, to create a local connection, the eXtremeDB database must be created in shared memory (not conventional memory) so that it can be accessed by more than one application (at a minimum, the eXtremeSQL application and the ODBC driver). So click the upper radio button and type the database name to connect to and click “Finish” to complete the DSN definition.
The screen below shows the specification for connecting to the TPC sample database.
To connect to the database from an eXtremeSQL ODBC application (see for example
odbc\samples\tpcodbc.c), specify the database name as the second parameter of the ODBC functionSQLConnect(). For example:SQLRETURN SQL_API SQLConnect( SQLHDBC hDbc, SQLCHAR *dsnName, SQLSMALLINT nameLength1, SQLCHAR *userName, SQLSMALLINT nameLength2, SQLCHAR *authentication, SQLSMALLINT nameLength3 )The nameLength1 parameter should be either the length of the dsnName argument, or SQL_NTS. The parameters after nameLength1 are ignored since eXtremeSQL uses an embedded database and doesn’t have a concept of “users”.
Note that the dsnName argument is the same name that was given to the eXtremeSQL API function
engine.open()or the eXtremeDB API functionmco_db_open_dev(). So, for the TPC sample, the database is opened as follows:engine.open("tpcdb", tpcdb_get_dictionary(),DATABASE_SIZE,PAGE_SIZE,MAP_ADDRESS);Consequently the
SQLConnect()call isSQLConnect( hDbc, “tpcdb”, SQL_NTS, 0, 0, 0, 0);Now, to run the SDK sample programs
tpcandtpcodbcfirst starttpcas follows:tpc -clients 1 -tpc 100000The
tpcprogram, acting as the database server, creates the in-memory database in shared memory and runs 100,000 iterations of the “TPC” test. When the test has completed wait (do not press the Enter key) to hold thetpcprocess (and its database) in memory. Now the ODBC driver can access thetpcdbdatabase. Start thetpcodbcclient program as follows:tpcodbc -tpc 100000 -db tpcdbThis command line instructs the ODBC client program to run 100,000 iterations of the “TPC” test and will display results similar to
tpcbecause they both access the same database on the local computer. The difference is simply thattpcaccesses the database directly via the eXtremeSQL API whiletpcodbcaccesses it through the ODBC driver.
Note that a subtle error can be introduced by copying and pasting the above commands into a console window. In some cases an unprintable ascii symbol is passed to the command line that causes the
tpcsample to startup incorrectly. And consequentlytpcodbccan’t connect to the database and throws an error. So we recommend typing the command lines manually.
Connecting to a remote database
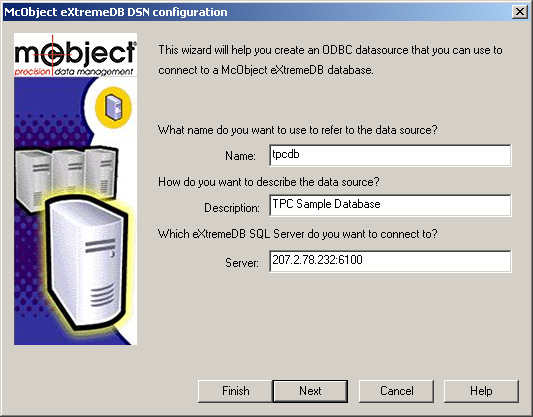
To connect to a remote database, enter the name and description in the McObject ODBC Setup dialog as described above. Then type the IP address of the system that is hosting the database followed by a colon (“:”) and the port number on which the eXtremeSQL server process is listening.
The example below specifies the
tpcdbdatabase used by the SDK samplessamples\native\sql\tpcandsamples\native\sql\tpcodbchosted on the computer with IP207.2.78.232that is listening on port6100:
The connection to the remote database is done through the xSQL utility, which plays the role of the database server.
To demonstrate the remote connection, start the application on the host computer that will create the database. Assuming the IP address of the host computer is
207.2.78.232and using again the SDK sample programstpcandtpcodbcfirst starttpcas follows:tpc -clients 1 -tpc 100000The
tpcsample creates the database with the following function call:engine.open("tpcdb", tpcdb_get_dictionary(),DATABASE_SIZE,PAGE_SIZE,MAP_ADDRESS);As in the local connection example above, the database named
tpcdbwill be placed in shared memory, and the program runs 100,000 iterations of the “TPC” test. When the test has completed wait (do not press the Enter key) to hold thetpcprocess (and its database) in memory.Next, on the same computer, start xSQL which will provide remote access to the in-memory database:
xsql tpcdb:6100This command starts xSQL, instructs it to open the
tpcdbdatabase and to listen on port6100for remote processes wanting to connect to the database.Finally, on another computer on the network, start the
tpcodbcclient program as follows:tpcodbc -tpc 100000 -db 207.2.78.232:6100This command line instructs the program to run 100,000 iterations of the “TPC” test, opening the ODBC data source name
207.2.78.232:6100which is, of course, the xSQL process running on the host computer and listening on port6100. The C source code intpcodbcestablishes the ODBC connection as follows:database = argv[i]; // extract the data source name from the command line SQLAllocEnv(&hEnv); // allocate the environment handle SQLAllocConnect(hEnv, &hDbc); // allocate the connection handle // connect to the data source (McObject ODBC driver) SQLConnect(hDbc, database, SQL_NTS, NULL, 0, NULL, 0);Now
tpcodbcwill display the results, although slower thantpcdue to latency in the network subsystem processing the data transfer between the ODBC driver and the eXtremeSQL remote server. (If the application appears to hang it may be advisable to reduce the number of tests by the command line argument, e.g.: “-tpc 100”.)Connection attributes
It is possible extract connection attributes from the connection string. The following attributes are supported:
DRIVER- the eXtremeDB driver nameDSN- DSN recordSERVER- the address or addresses divided by comma of the RSQL servers to connect toSQL_N_REPLICAS- the number of replicas in the connection through the DistributedSqlEngine (corresponds to thenReplicasargument when calling theDistributedSqlEngine::open() C++ API)SQL_CONNECT_ATTEMPTS- the number of attempts to connect (corresponds to themaxConnectAttemptsargument when calling theRemoteSqlEngine::open()or)DistributedSqlEngine::open()C++ APIsSQL_CONNECT_TIMEOUT- server connection timeout (corresponds to theconnectTimeoutargument when calling theRemoteSqlEngine::open()or)DistributedSqlEngine::open()C++ APIsSQL_READ_TIMEOUT- server reply timeout (corresponds to thereadTimeoutargument when calling theRemoteSqlEngine::open()or)DistributedSqlEngine::open()C++ APIsDATABASE- the database name in the connections to the shared memory databaseWhen the
DSNattribute is used, all connection data is taken from the DSN record. However if theSERVER,SQL_N_REPLICAS,SQL_CONNECT_ATTEMPTSandDATABASEattributes are specified separately, their values overwrite DSN values.If the
DSNattribute is not used, either theDRIVERor theSERVERmust be specified for the remote (RSQL) connection and theDATABASEattribute must be specified to establish a shared memory database connection.The driver name (
DRIVER) for x32 systems is "McObject eXtremeDB driver" and for х64 systems it is "McObject eXtremeDB 64bit driver". The odbcad32 utility reflects these names.Following is a C# code snippet showing how attributes can be specified:
// Manually specify the driver and two servers addresses (distributed RSQL connection)String connectionString = "Driver={McObject eXtremeDB driver};SERVER=localhost:6001,localhost:6002;"; // Get most of data source attributes from DSN 'xsql_dsn' but override the SERVER attribute //String connectionString = "DSN=xsql_dsn;SERVER=localhost:6001;";// Get all data source attributes from DSN 'xsql_dsn'//String connectionString = "DSN=xsql_dsn";System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection dbconn; dbconn = new System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection(connectionString);